- With standard equipment
- With safety pack
Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
Find more information in the Rating Validity tab of the assessment
- See More
- See More
- See More
- See More
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
 Passenger
Passenger
 Driver
Driver
 Rear Passenger
Rear Passenger
 Driver
Driver
 Car
Car
 Pole
Pole
 Rear Seat
Rear Seat
 Front Seat
Front Seat
-
Approaching a stationary car: Left Offset
-
Approaching a stationary car: No Offset
-
Approaching a stationary car: Right Offset
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor


Passenger
outboard
center
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option
Not Available
-
i-Size CRS
-
ISOFIX CRS
-
Universal Belted CRS
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
| Seat Position | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | 2nd row | |||
| Passenger | Left | center | Right | |
| Maxi Cosi 2way Pearl & 2wayFix (rearward) (iSize) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi 2way Pearl & 2wayFix (forward) (iSize) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Kid X2 i-Size (iSize) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Flex FIT i-Size (iSize) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix & FamilyFix (ISOFIX) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Kid X4 ISOfix (ISOFIX) | ||||
| Britax Römer Duo Plus (ISOFIX) | ||||
| Britax Römer KidFix XP (ISOFIX) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix (Belt) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix & EasyBase2 (Belt) | ||||
| Britax Römer King II LS (Belt) | ||||
| Britax Römer KidFix XP (Belt) | ||||
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
In the frontal offset test, dummy readings showed good or adequate protection of all critical body areas for both the 6 and 10 year children. In the side barrier test, protection was good for all critical parts of the body, except for the head of the 10 year child, which was rated as adequate, based on readings of head acceleration. The CLA has a system that automatically recognises when a rearward-facing child restraint has been put in the front passenger seat and deactivates the airbag for that seating position. Mercedes-Benz showed that the system worked robustly and it was rewarded. All of the restraint types for which the CLA is designed could be properly installed and accommodated.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
Head Impact 20.3 Pts
Pelvis Impact 6.0 Pts
Leg Impact 6.0 Pts
| System Name | Active Brake Assist | ||
| Type | Auto-Brake with Forward Collision Warning | ||
| Operational From | 7 km/h | ||
| PERFORMANCE | | |||
-
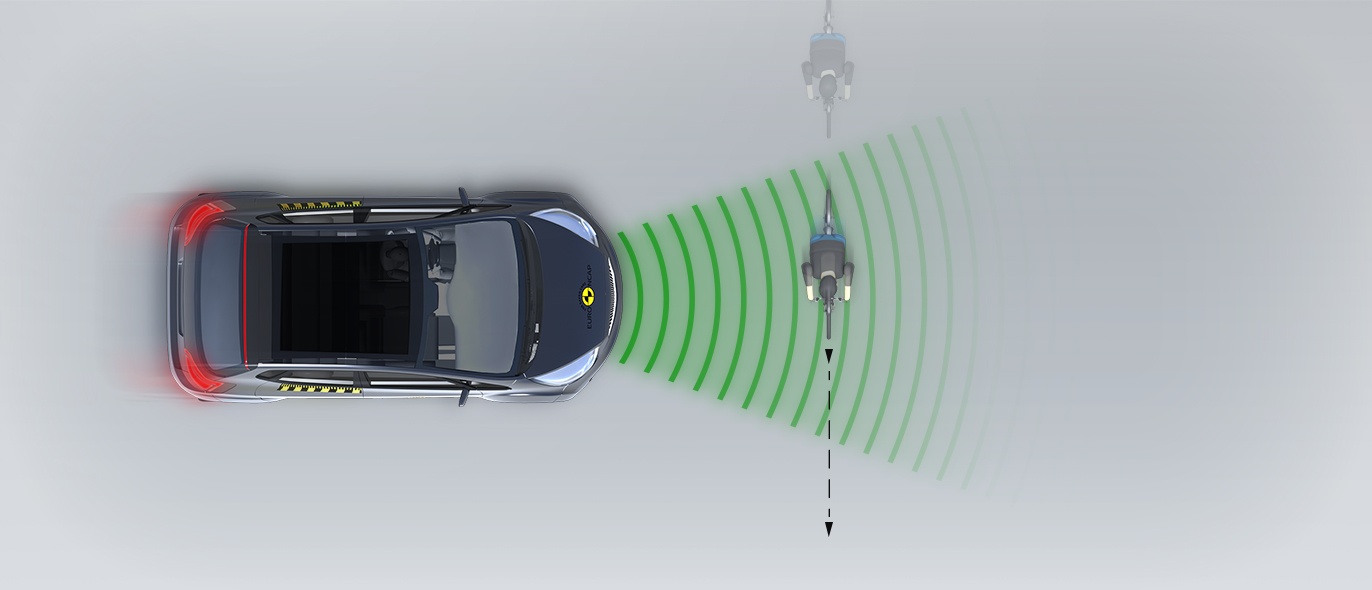
Approaching a crossing cyclist
-
Cyclist along the roadside
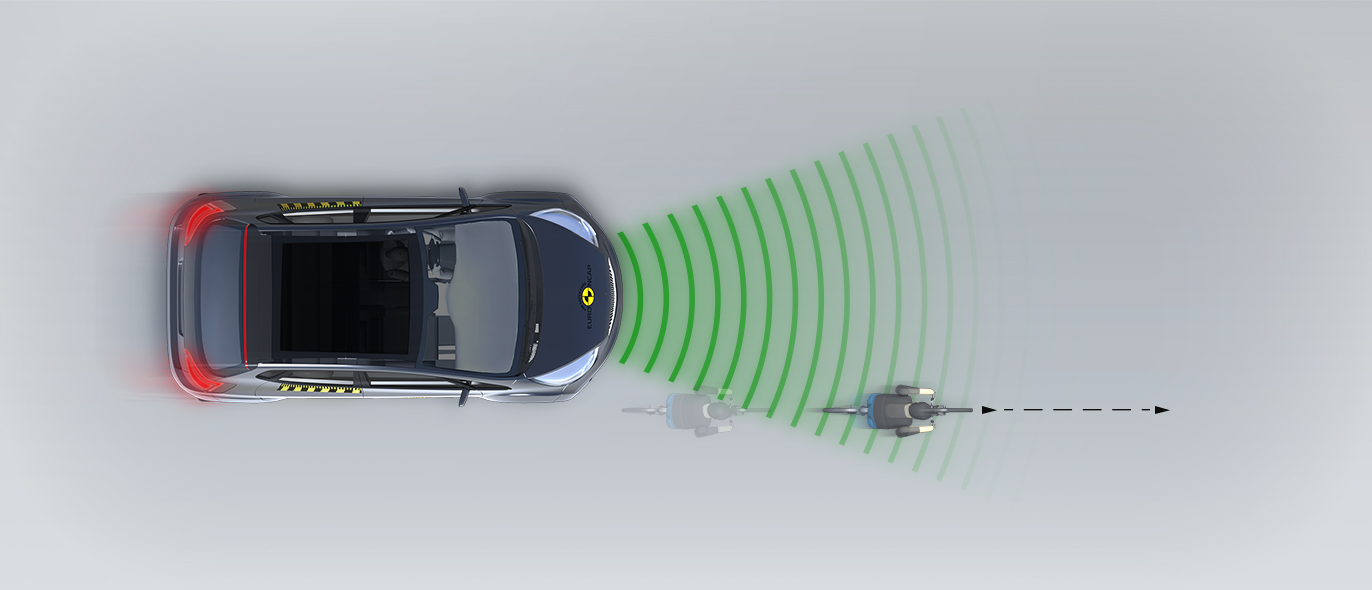
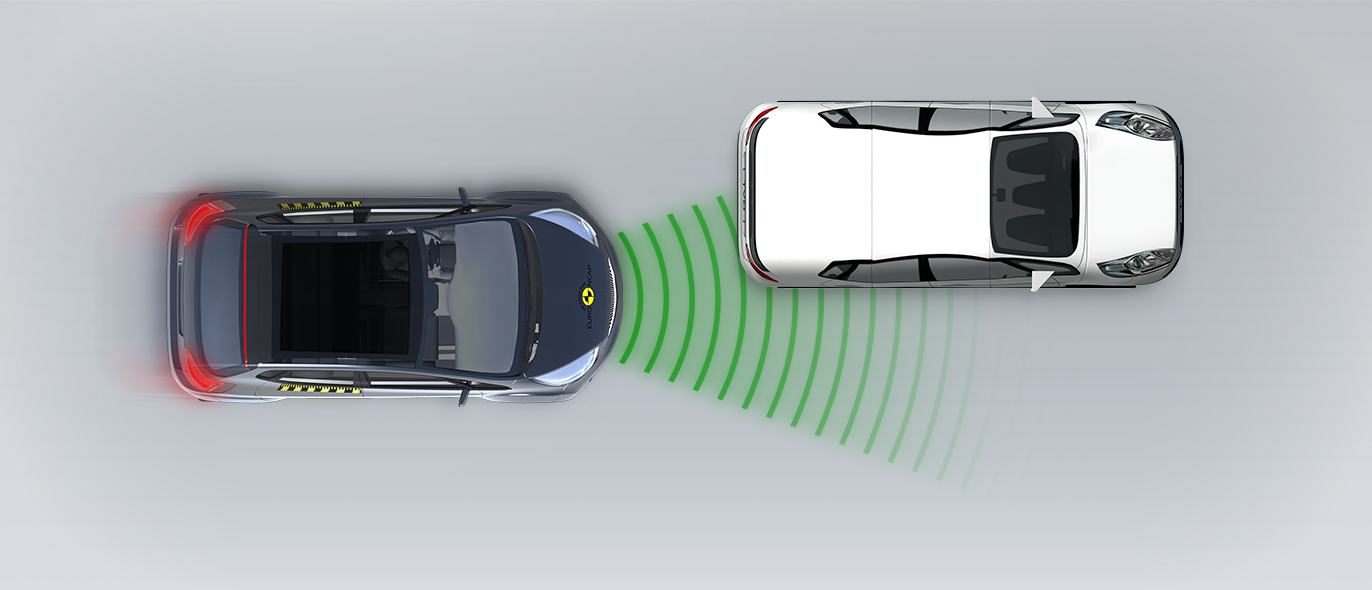
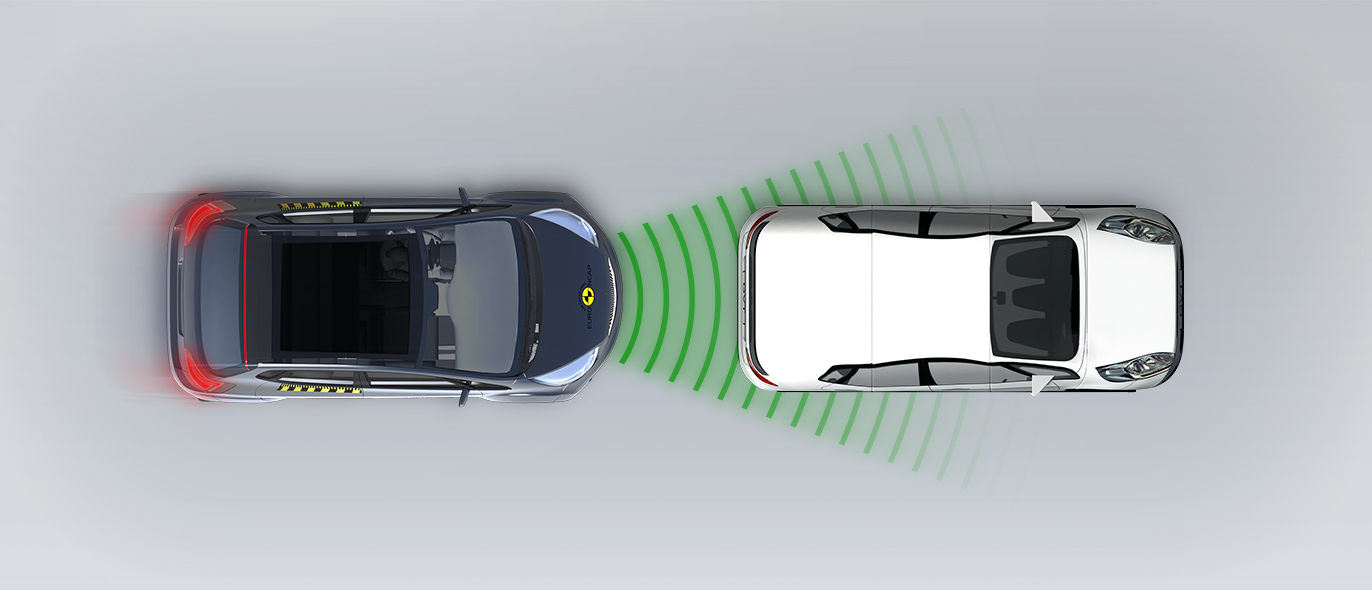
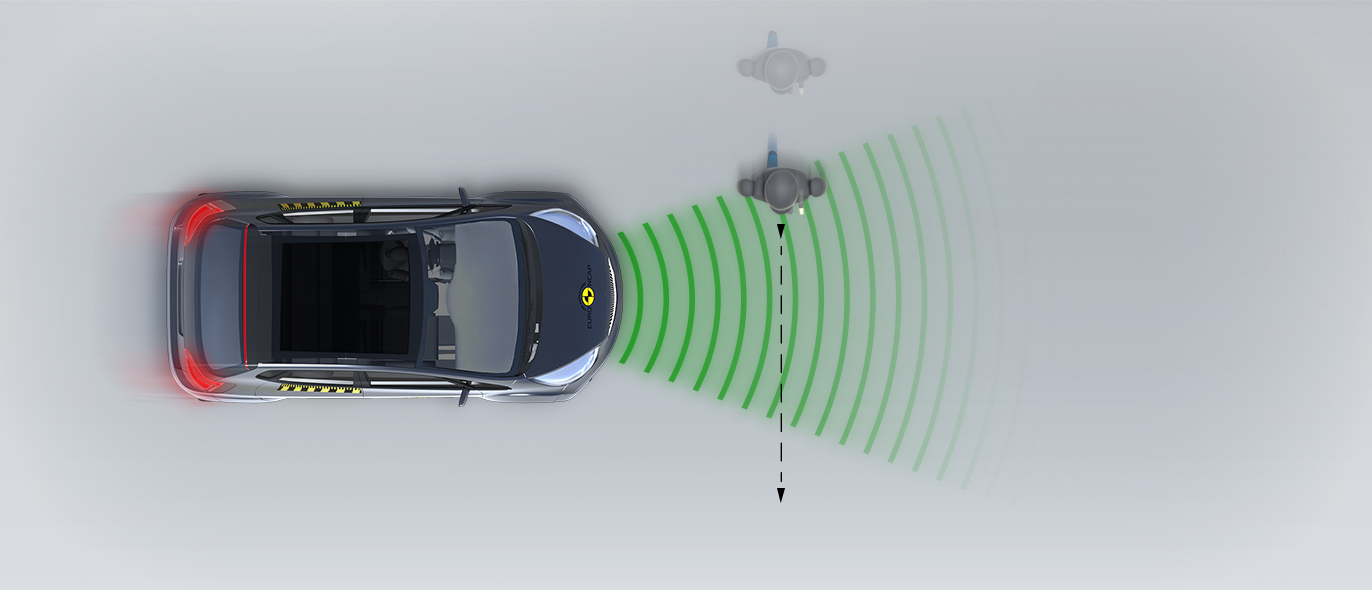
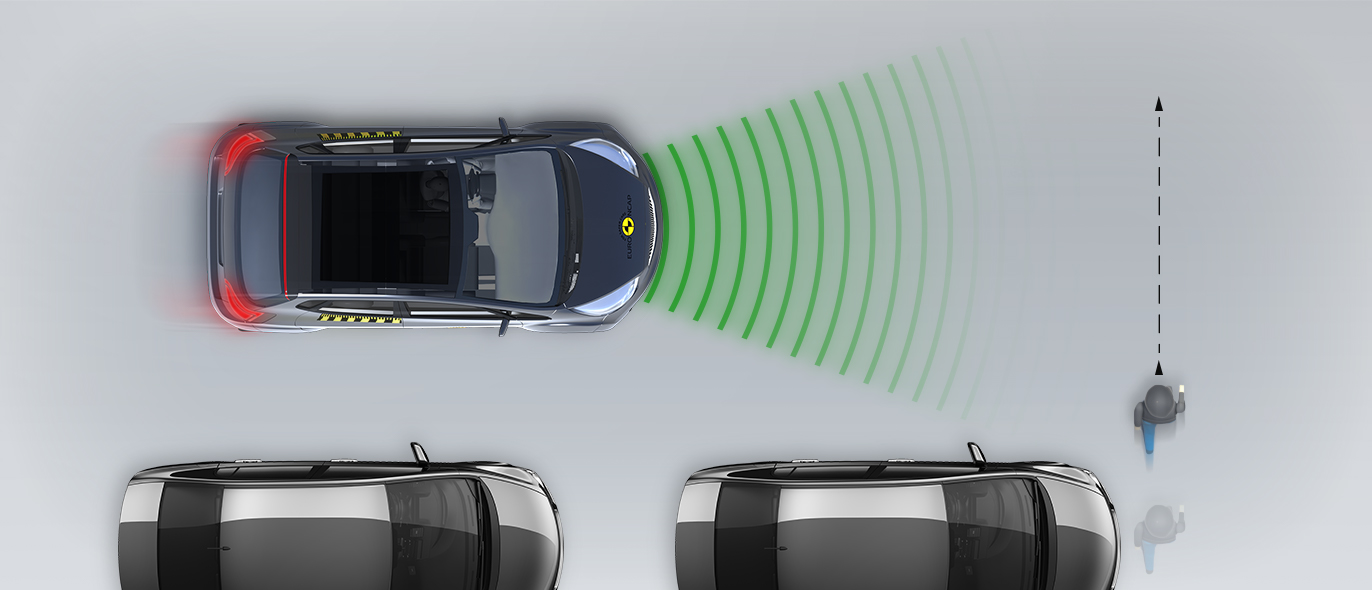
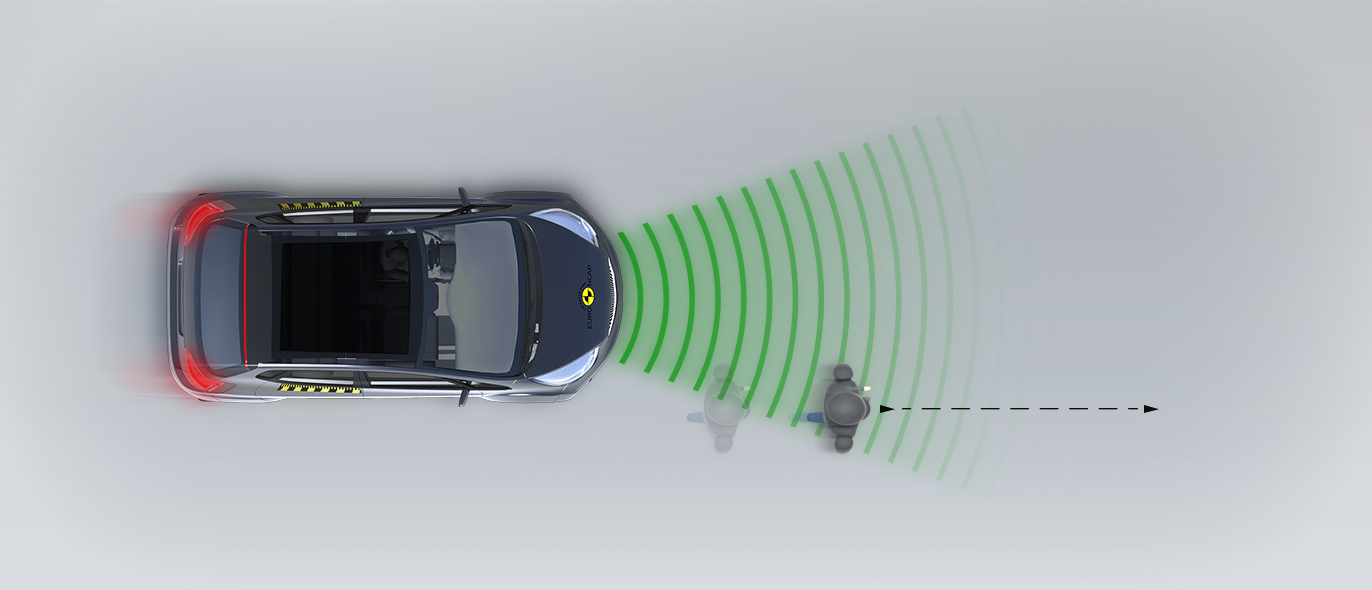
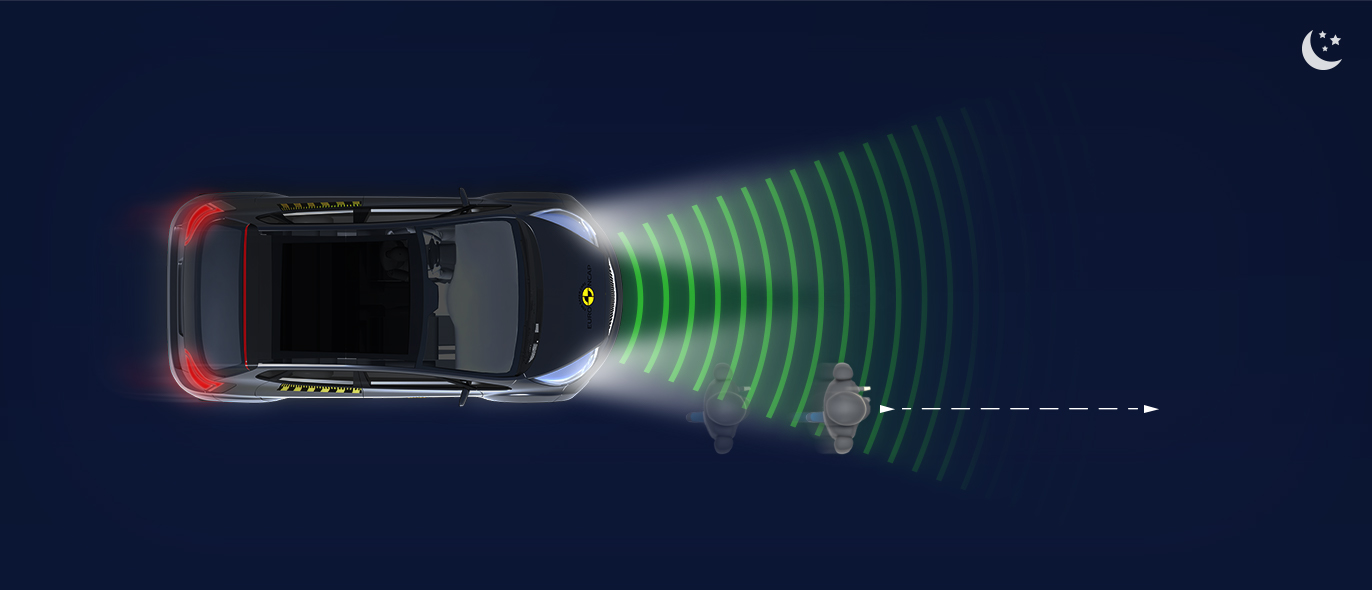
The CLA has an active, deployable bonnet. Sensors in the bumper detect when a pedestrian has been struck and actuators lift the bonnet surface to provide greater clearance to the stiff structures in the engine compartment. Mercedes-Benz showed that the system worked robustly for different pedestrian statures and across a wide range of speeds, so tests were performed with the bonnet in the raised position. Protection was good at almost all test locations on the bonnet. Protection was also good for the leg and pelvis areas of a struck pedestrian. The AEB system performed well in tests both of its pedestrian detection and its response to cyclists, with collisions avoided in nearly all test scenarios.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
| System Name | Speed Limit Assist |
| Speed Limit Information Function | Camera based |
| Speed Control Function | System advised (accurate to 5km/h) |
| Applies To | All Seats | ||
| Warning | Driver Seat | Front Passenger(s) | Rear Passenger(s) |
| Visual | |||
| Audible | |||
| Occupant Detection | |||
|
|||
| System Name | Active Lane Keeping Assist |
| Type | ELK + LKA (including LDW) |
| Operational From | 60 km/h |
| Performance | |
| Emergency Lane Keeping | |
| Lane Keep Assist | |
| Human Machine Interface | |
| System Name | Active Brake Assist | |||
| Type | Autonomous Emergency Braking and Forward Collision Warning | |||
| Operational From | 7 km/h | |||
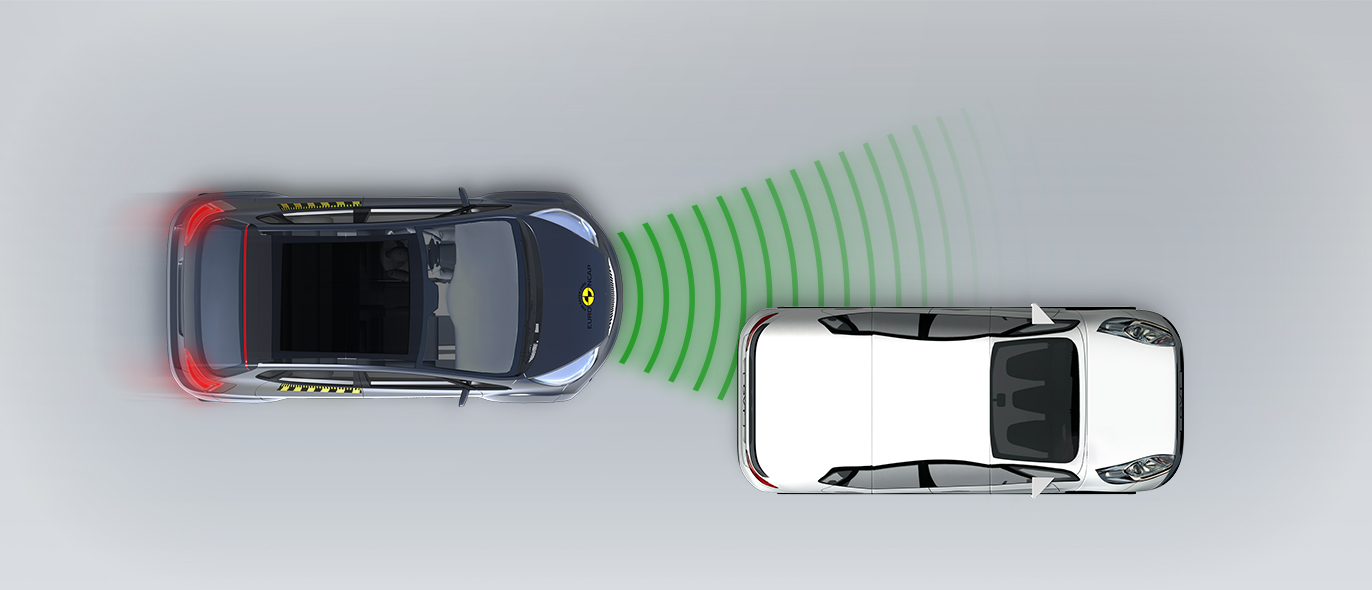
The AEB system performed well in tests of its functionality at highway speeds. The lane assistance system performed marginally, with adequate performance for lane keeping assistance and emergency lane keeping but lacking a blind-spot monitoring system. The speed assistance system, comprising a camera-based speed limit detection system and driver-set speed limiter, was rated as good. The car has a seatbelt reminder system as standard for front and rear seats.
- Specifications
- Safety Equipment
- Videos
- Advanced Rewards
- Rating Validity
Specifications
Tested Model Mercedes-Benz CLA 180, AMG Line, LHD
Body Type - 4 door saloon
Year Of Publication 2019
Kerb Weight 1395kg
VIN From Which Rating Applies - all CLAs
Class Small Family Car
Safety Equipment
Note: Other equipment may be available on the vehicle but was not considered in the test year.
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Fitted to the vehicle as part of the safety pack
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option or as part of the safety pack
Not available
Not applicable
Videos
Advanced Rewards
Rating Validity
Variants of Model Range
| Body Type | Engine & Transmission | Model Name/Code | Drivetrain | Rating Applies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHD | RHD | ||||
| 4 door saloon | 1.46 diesel | CLA 180 d | 4 X 2 |  |
 |
| 4 door saloon | 1.95 diesel | CLA 200 d / CLA 220 d | 4 X 2 |  |
 |
| 4 door saloon | 1.95 diesel | CLA 220d 4MATIC | 4 X 4 |  |
 |
| 4 door saloon | 1.33 petrol | CLA 180* / CLA 200 | 4 X 2 |  |
 |
| 4 door saloon | 1.99 petrol | CLA 220 / CLA 250 | 4 X 2 |  |
 |
| 4 door saloon | 1.99 petrol |
CLA 220 4MATIC / CLA 250 4 MATIC |
4 X 4 |  |
 |
* Tested variant
Table applies to Shooting Brake variants



Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
The Mercedes-Benz CLA shares its active safety technology with the A-Class, assessed by Euro NCAP in 2018. Hardware is the same and the two cars' systems perform equivalently. Accordingly, active safety results are based on those of the A-Class. As the front seats and head restraints are also identical, the results of the A-Class have also been used for rear-end whiplash protection. All full-scale crash tests have been repeated.
 Share
Share











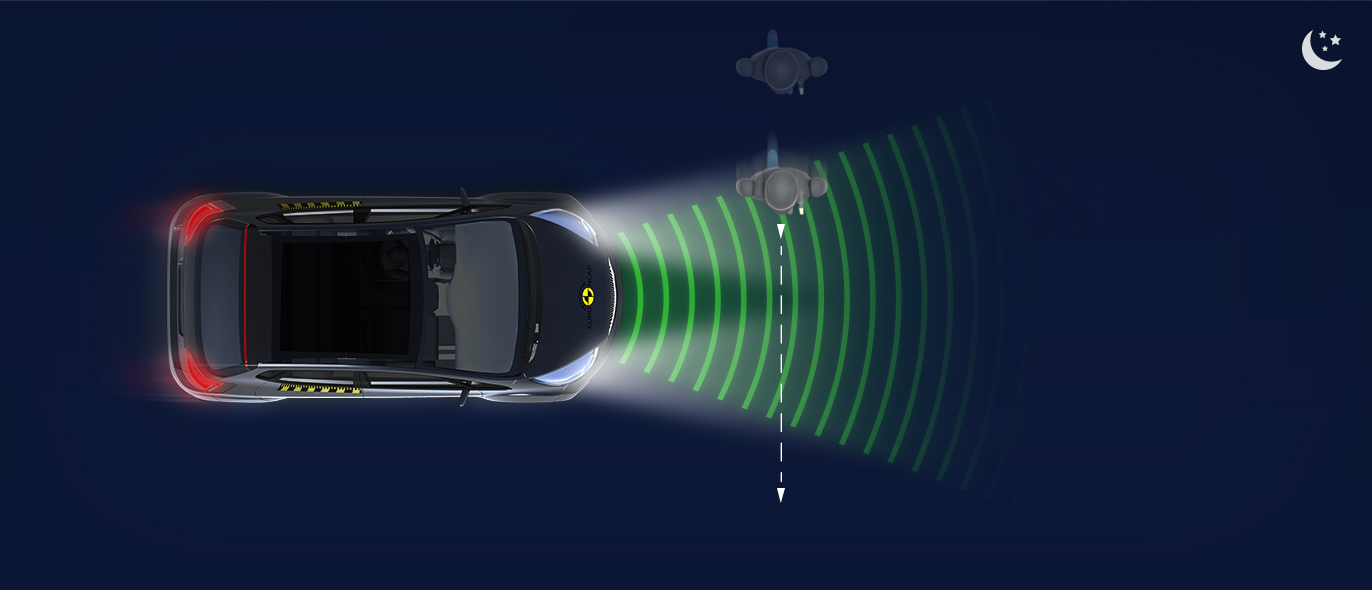
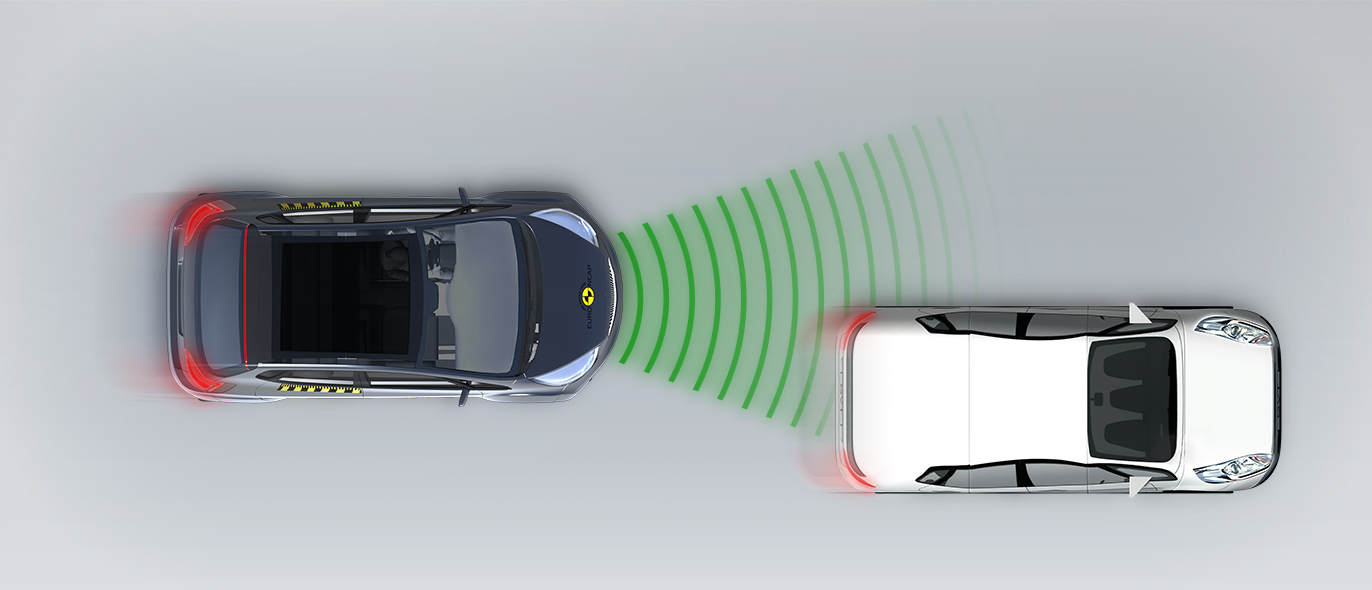
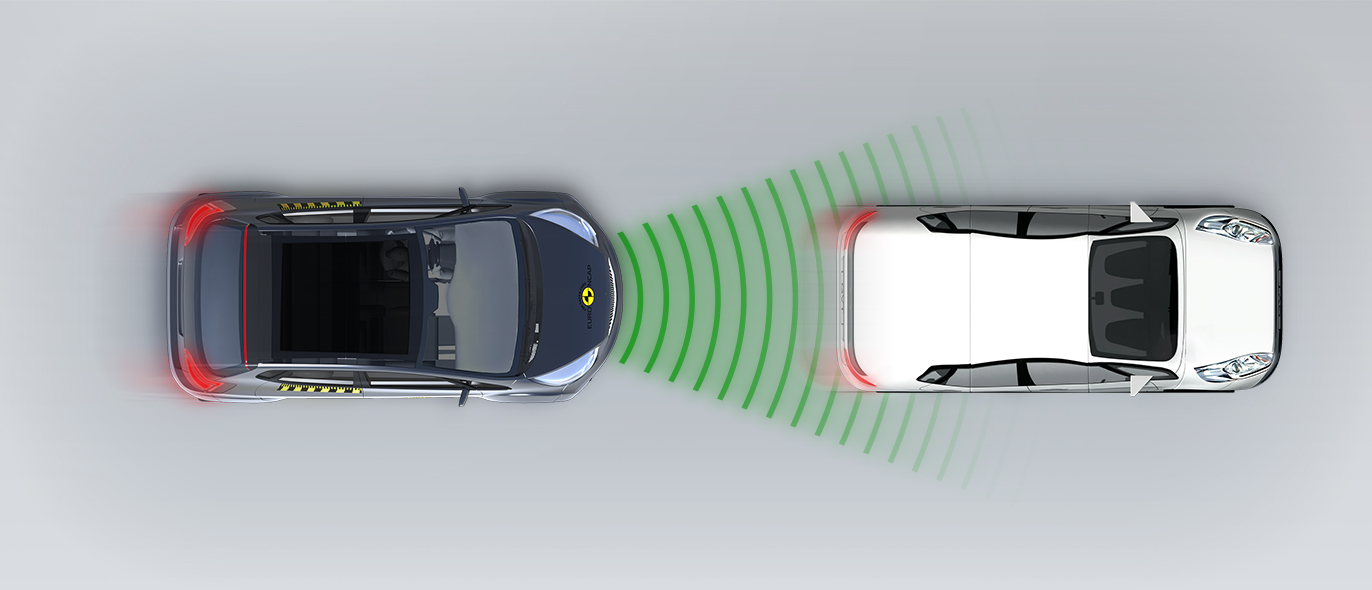
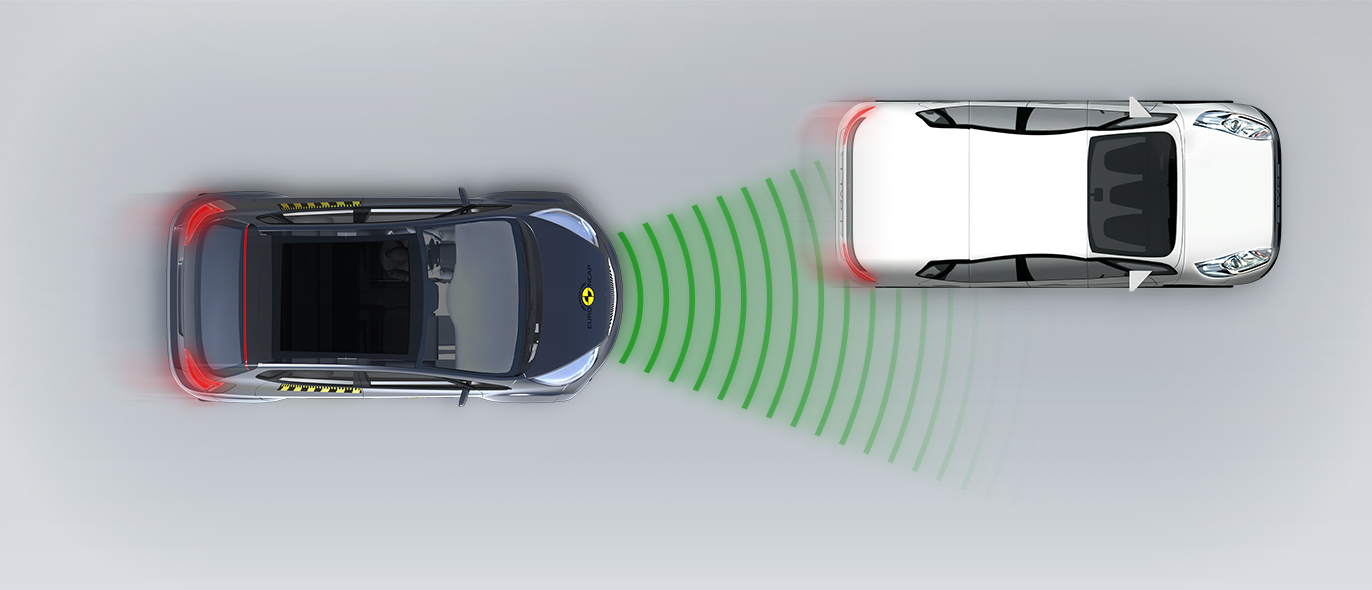
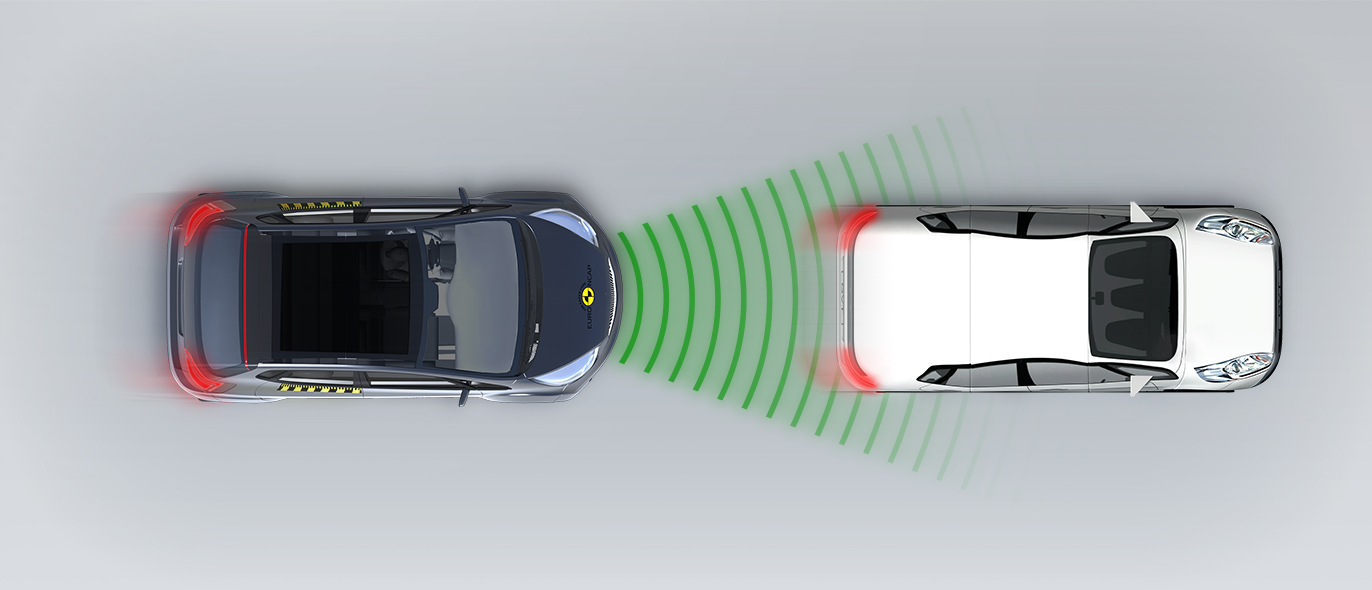
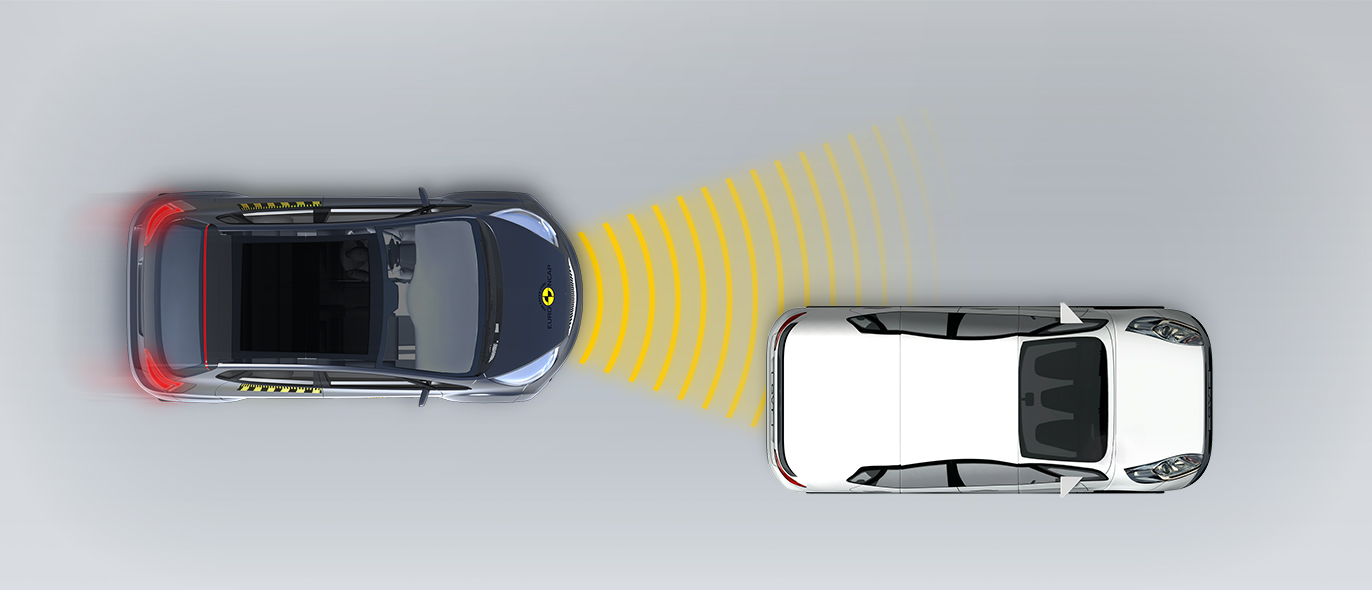
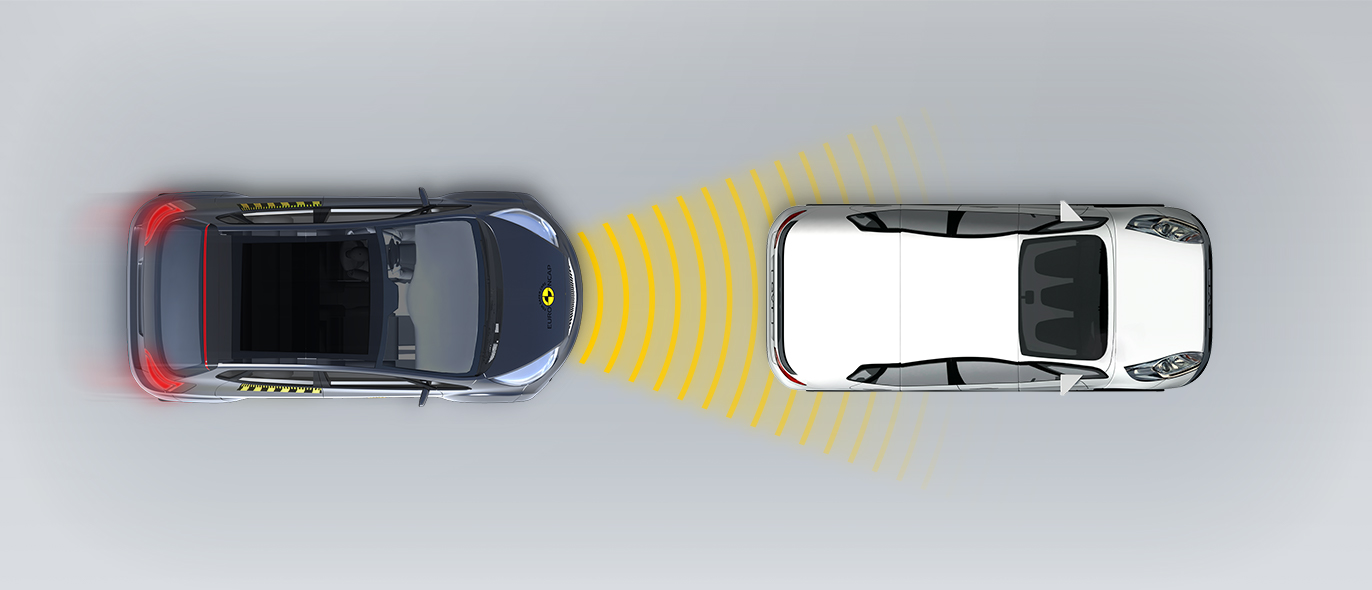
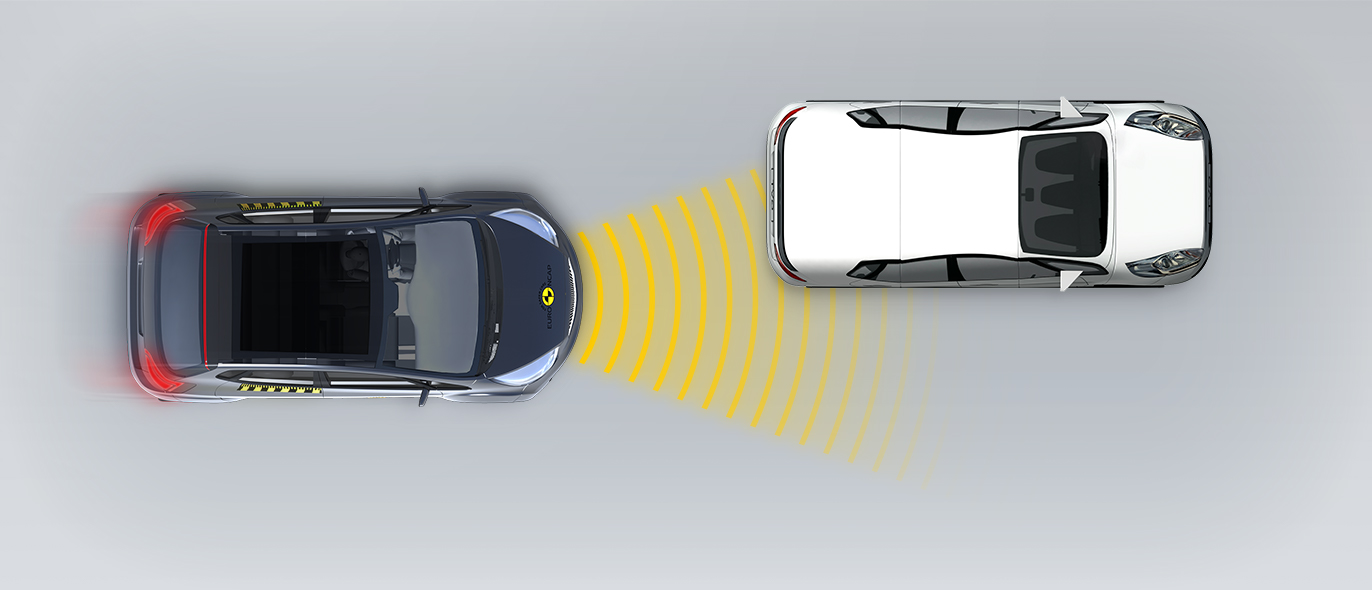

The passenger compartment of the CLA remained stable in the frontal offset test. Dummy readings indicated good protection of the knees and femurs of both the driver and passenger. Mercedes-Benz showed that a similar level of protection would be provided to occupants of different sizes and to those sitting in different positions. In the full-width rigid barrier test, protection of all critical body areas was good or adequate for both the driver and the rear passenger. In the side barrier impact, dummy readings showed good protection of all body areas. However, the rear door on the impacted side of the car opened during the test and the score was penalised for the risk of occupant ejection. In the more severe side pole test, protection of the chest was adequate and that of other critical body regions was good. Tests on the front seats and head restraints demonstrated good protection against whiplash injuries in the event of a rear-end collision. A geometric assessment of the rear seats also indicated good whiplash protection. The autonomous emergency braking (AEB) system performed well in tests of its functionality at the low speeds, typical of city driving, at which many whiplash injuries are caused, with collisions avoided or mitigated in all test scenarios.